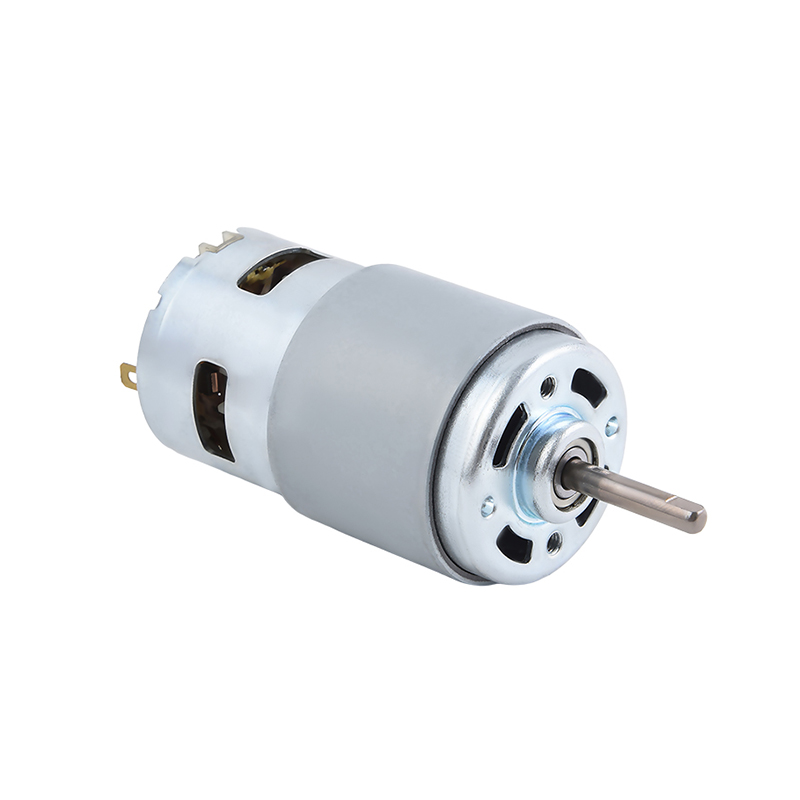
Top Applications of Brush DC Motors in Consumer and Industrial Products
 2026.02.05
2026.02.05
 Industry News
Industry News
Brush DC Motor Applications in Consumer Electronics and Smart Devices
Brush DC Motor Role in Consumer Electronics Design
Brush DC Motor plays a critical role in the design and functionality of a wide range of consumer electronics, particularly in products that require compact size, simple control, and cost-effective motion solutions. In consumer electronics, product designers often prioritize reliability, manufacturability, and low system complexity, making Brush DC Motor a preferred choice for many electromechanical functions. The ability of a Brush DC Motor to operate directly from a DC power source without complex drive electronics simplifies circuit design and reduces the overall bill of materials.
In many consumer electronics, motion requirements are relatively straightforward, such as rotational movement, linear actuation through gear mechanisms, or intermittent operation. Brush DC Motor meets these requirements efficiently due to its predictable speed–voltage relationship and high starting torque. This makes it suitable for applications where rapid response and consistent mechanical output are required without advanced motor control algorithms.
Another important factor is scalability. Brush DC Motor designs can be easily adapted to different sizes, power levels, and voltage ratings, enabling manufacturers to reuse motor platforms across multiple product lines. This adaptability supports mass production strategies common in consumer electronics markets, where cost control and supply chain stability are essential.
Brush DC Motor Applications in Portable Consumer Devices
Brush DC Motor is widely used in portable consumer devices due to its compact form factor and compatibility with battery-powered systems. Devices such as handheld fans, electric shavers, personal massagers, portable vacuum cleaners, and grooming tools frequently rely on Brush DC Motor to deliver mechanical motion within tight space constraints.
Battery-powered consumer devices often operate at low voltages, typically ranging from 1.5V to 12V. Brush DC Motor can operate efficiently within this voltage range, making it ideal for products powered by alkaline batteries, lithium-ion cells, or rechargeable battery packs. The motor’s ability to deliver sufficient torque at low voltage allows designers to avoid complex voltage-boosting circuits.
In portable electronics, weight and noise levels are also important considerations. Small Brush DC Motor variants, including coreless and iron-core designs, can be optimized for low inertia and smooth operation. This enables quieter performance, which is particularly important in personal care devices and wearable consumer electronics.
The simple speed control of Brush DC Motor through pulse-width modulation or voltage adjustment allows manufacturers to implement multiple operating modes without significantly increasing system complexity. This flexibility is frequently used in consumer devices that offer adjustable speed, intensity, or power settings.
Brush DC Motor Use in Audio-Visual Consumer Electronics
In audio-visual consumer electronics, Brush DC Motor is commonly used to perform auxiliary mechanical functions that support the primary electronic system. Examples include optical disc drives, camera lens mechanisms, projector cooling systems, and motorized adjustment components in televisions and home theater equipment.
Optical drive mechanisms historically relied on Brush DC Motor for disc rotation, tray loading, and laser positioning systems. The precise yet simple control of Brush DC Motor allows for smooth acceleration and deceleration, which is essential for maintaining media stability and reducing vibration during operation.
In cameras and imaging devices, Brush DC Motor is often integrated into autofocus systems, zoom mechanisms, and shutter assemblies. While more advanced devices may use stepper or brushless motors, Brush DC Motor remains prevalent in cost-sensitive consumer cameras due to its lower cost and straightforward integration.
Cooling systems in audio-visual equipment also frequently employ Brush DC Motor-driven fans. These fans provide thermal management for internal electronic components, ensuring stable operation and extended product lifespan. The predictable speed characteristics of Brush DC Motor simplify thermal control strategies, allowing designers to balance airflow, noise, and power consumption.
Brush DC Motor Applications in Smart Home Devices
Brush DC Motor is extensively applied in smart home devices where mechanical actuation is required to interact with the physical environment. Products such as smart locks, automated curtains, smart blinds, robotic cleaning devices, and adjustable smart furniture incorporate Brush DC Motor to achieve controlled movement.
Smart home devices often integrate wireless connectivity, sensors, and microcontrollers. Brush DC Motor complements these systems by offering a motion solution that can be easily controlled via simple driver circuits. This allows developers to focus on software and connectivity features without the need for complex motor control firmware.
In smart locks and access control systems, Brush DC Motor provides the torque needed to engage and disengage locking mechanisms. Its ability to deliver high starting torque ensures reliable operation even under varying mechanical loads or slight misalignments.
Robotic vacuum cleaners and floor-cleaning devices commonly use multiple Brush DC Motor units for wheel drive, brush rotation, and suction fan operation. These motors are selected for their durability, availability, and ease of replacement, which aligns with the high-volume production and service requirements of smart home appliances.
Brush DC Motor Integration in Wearable and Personal Electronics
Wearable and personal electronics increasingly incorporate mechanical feedback and motion features that rely on Brush DC Motor technology. Devices such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, and haptic feedback accessories utilize miniature Brush DC Motor designs to generate vibration alerts and tactile responses.
In haptic systems, Brush DC Motor drives eccentric rotating masses or linear vibration mechanisms to create perceptible feedback. The rapid response and controllable speed of Brush DC Motor enable precise vibration patterns that enhance user interaction and notification awareness.
Personal electronics often demand extremely compact and lightweight components. Micro Brush DC Motor designs, including coreless variants, are well-suited for these applications due to their high efficiency-to-size ratio. These motors can be integrated into thin enclosures without significantly impacting device ergonomics.
Power efficiency is another critical factor in wearable electronics. Brush DC Motor designs optimized for low current consumption help extend battery life, particularly in devices that operate continuously or require frequent vibration feedback throughout the day.
Brush DC Motor Applications in Office and Commercial Electronics
Office and commercial electronics represent another important segment where Brush DC Motor is widely applied. Printers, scanners, copiers, paper shredders, and automated document handling systems rely on Brush DC Motor for paper feeding, roller drive mechanisms, and carriage movement.
In printing systems, Brush DC Motor drives rollers that transport paper through the printing path. The consistent speed output of Brush DC Motor ensures accurate paper alignment and timing, which is essential for print quality and mechanical reliability.
Office electronics often operate in shared environments where noise levels must be controlled. Brush DC Motor designs can be paired with appropriate gearboxes and damping materials to reduce operational noise while maintaining sufficient torque output.
The ease of maintenance and replacement associated with Brush DC Motor is also beneficial in commercial environments. Service technicians can quickly diagnose and replace motor components without specialized tools or advanced calibration procedures.
Brush DC Motor Role in Human–Machine Interaction Devices
Human–machine interaction devices frequently incorporate Brush DC Motor to provide motion, feedback, or mechanical assistance. Examples include motorized control knobs, adjustable displays, automated input devices, and assistive consumer technologies.
Motorized controls enhance user experience by providing smooth, responsive adjustments that align with digital input commands. Brush DC Motor enables these features through simple control schemes that integrate easily with microcontrollers and user interface systems.
Assistive devices designed for accessibility often rely on Brush DC Motor to provide controlled movement or force amplification. These applications benefit from the predictable performance characteristics of Brush DC Motor, which support safe and reliable operation in consumer-facing products.
Brush DC Motor Considerations for Consumer Electronics Manufacturing
From a manufacturing perspective, Brush DC Motor offers advantages that align with the demands of consumer electronics production. The mature supply chain for Brush DC Motor components ensures stable availability, standardized quality control processes, and competitive pricing.
Design engineers can select from a wide range of standardized Brush DC Motor models, reducing development time and simplifying regulatory compliance. The established testing methods for Brush DC Motor performance, including speed, torque, and lifetime testing, support consistent product quality.
Automation compatibility is another important consideration. Brush DC Motor can be easily integrated into automated assembly lines, where repeatability and process efficiency are critical. The standardized form factors and mounting options of Brush DC Motor facilitate seamless integration into diverse product designs.
Brush DC Motor Use Cases in Household Appliances
Brush DC Motor Importance in Household Appliance Systems
Brush DC Motor is a foundational electromechanical component in a wide range of household appliances that require controlled rotational motion, airflow generation, fluid movement, or mechanical actuation. Household appliances are typically designed for long operating hours, repeated duty cycles, and operation under varying load conditions, making the predictable behavior of Brush DC Motor particularly valuable in this sector.
In many household appliance systems, the motor is not the primary selling feature but a critical enabler of functionality. Brush DC Motor supports core appliance operations while allowing manufacturers to balance cost, performance, and reliability. The simplicity of Brush DC Motor control, combined with its ability to operate directly from rectified AC or low-voltage DC supplies, aligns well with the electrical architectures commonly used in household appliances.
Appliance designers often prioritize robustness and ease of integration. Brush DC Motor offers standardized mounting options, well-understood performance curves, and broad compatibility with mechanical transmission components such as gearboxes, belts, pulleys, and impellers. These characteristics reduce design risk and development time across appliance product families.
Brush DC Motor Applications in Kitchen Appliances
Brush DC Motor is extensively used in kitchen appliances that require rotational motion, mixing, cutting, or airflow generation. Devices such as blenders, mixers, food processors, coffee grinders, electric can openers, and juicers rely on Brush DC Motor to deliver sufficient torque and speed across a range of operating conditions.
In blending and mixing applications, Brush DC Motor drives rotating blades through direct coupling or gear reduction mechanisms. The high starting torque of Brush DC Motor allows it to handle dense food materials, varying viscosity, and sudden load changes without stalling. Voltage-based speed control enables multiple operating modes, allowing users to select different processing intensities.
Coffee machines and grinders frequently integrate Brush DC Motor to drive burrs, pumps, or internal mechanisms. In these systems, Brush DC Motor provides consistent rotational speed, which directly influences grind size uniformity or fluid pressure stability. The predictable electrical characteristics of Brush DC Motor simplify integration with appliance control boards.
Kitchen ventilation systems, such as range hoods and extractor fans, also rely on Brush DC Motor-driven fan assemblies. These motors are selected for their ability to provide stable airflow, acceptable noise levels, and long operational life under continuous or intermittent use.
Brush DC Motor Use in Cleaning Appliances
Cleaning appliances represent one of the most significant application areas for Brush DC Motor in household environments. Products such as vacuum cleaners, robotic vacuum systems, carpet cleaners, and handheld cleaning tools incorporate multiple Brush DC Motor units to perform different mechanical tasks.
In vacuum cleaners, Brush DC Motor is used to drive suction fans, rotating brush rollers, and wheel assemblies. The suction fan motor requires high rotational speed to generate sufficient airflow and negative pressure. Brush DC Motor designs optimized for high-speed operation are well-suited for this purpose, offering strong airflow performance with relatively simple control circuits.
Brush rollers in vacuum cleaners rely on Brush DC Motor to agitate carpets and lift debris. These motors are typically paired with gear reduction systems to deliver controlled torque and consistent rotational speed. The durability of Brush DC Motor under dust exposure and repeated start-stop cycles is a key consideration in these applications.
Robotic cleaning devices often integrate multiple small Brush DC Motor units. Wheel drive motors enable navigation and obstacle handling, while additional motors power cleaning brushes and suction systems. The widespread availability and standardized sizing of Brush DC Motor components support modular robotic designs and scalable manufacturing.
Brush DC Motor Applications in Laundry Appliances
Laundry appliances, including washing machines and dryers, utilize Brush DC Motor for auxiliary functions that support core appliance operation. While main drum drive systems may use alternative motor technologies, Brush DC Motor is commonly employed for pumps, fans, valves, and dispensing mechanisms.
In washing machines, Brush DC Motor drives drain pumps that remove water from the drum during wash and spin cycles. These motors are selected for their ability to operate reliably in wet environments and handle particulate matter without significant performance degradation.
Detergent dispensing systems often use Brush DC Motor to actuate dosing mechanisms. The precise control of rotational movement allows accurate dispensing of liquid or powdered detergents based on program settings.
In dryers, Brush DC Motor drives airflow fans that circulate heated air through the drum. Stable fan speed is essential for consistent drying performance and thermal management. Brush DC Motor enables straightforward speed regulation based on temperature feedback and load conditions.
Brush DC Motor Use Cases in Home Comfort Appliances
Home comfort appliances, such as fans, air purifiers, humidifiers, and dehumidifiers, rely heavily on Brush DC Motor to generate airflow and control environmental conditions. These appliances often operate for extended periods, making motor reliability and efficiency important design considerations.
In electric fans, Brush DC Motor drives blade assemblies to produce airflow at adjustable speeds. Voltage-based or PWM control allows users to select airflow intensity while maintaining smooth motor operation. The linear speed response of Brush DC Motor simplifies control implementation.
Air purifiers and humidifiers use Brush DC Motor to drive fans and water circulation mechanisms. In humidifiers, the motor may power an impeller or ultrasonic water delivery system, ensuring consistent moisture output. Brush DC Motor designs optimized for low noise and steady operation are preferred in living space applications.
Dehumidifiers integrate Brush DC Motor to drive compressors, fans, and condensate pumps. These motors support continuous operation and must perform reliably under fluctuating temperature and humidity conditions.
Brush DC Motor Applications in Refrigeration Systems
Refrigeration appliances, including refrigerators and freezers, incorporate Brush DC Motor for multiple internal functions. While compressors may use specialized motor technologies, Brush DC Motor is commonly applied in evaporator fans, condenser fans, and ice-making mechanisms.
Evaporator fans circulate cold air within the refrigerator compartment, ensuring uniform temperature distribution. Brush DC Motor-driven fans provide stable airflow and can be controlled to optimize cooling efficiency and reduce frost formation.
Condenser fans use Brush DC Motor to dissipate heat from the refrigeration system. These motors must operate reliably in warm environments and withstand prolonged duty cycles. The robust construction of Brush DC Motor supports these operational demands.
Automatic ice makers often rely on Brush DC Motor to drive ejector mechanisms and water dispensing systems. The controlled rotational motion enables precise timing and coordination with refrigeration cycles.
Brush DC Motor Role in Small Household Utility Devices
Small household utility devices frequently incorporate Brush DC Motor to perform targeted mechanical tasks. Devices such as electric toothbrushes, hair dryers, sewing machines, and garment steamers depend on Brush DC Motor for motion generation.
Hair dryers use Brush DC Motor-driven fans to generate airflow across heating elements. The high-speed capability of Brush DC Motor enables compact fan designs that deliver strong airflow within small enclosures.
Electric toothbrushes and personal care devices utilize miniature Brush DC Motor units to produce oscillatory or rotational motion. These motors are designed for low voltage operation, compact size, and consistent performance over repeated daily use.
Sewing machines integrate Brush DC Motor to drive needle mechanisms and fabric feed systems. Speed control allows users to adjust sewing pace based on material type and task complexity.
Brush DC Motor Integration Considerations in Household Appliances
Integrating Brush DC Motor into household appliances requires careful consideration of electrical, mechanical, and environmental factors. Appliance designers must account for voltage compatibility, thermal management, and electromagnetic interference.
Brush DC Motor control circuits are typically designed to handle variable loads and protect against overcurrent conditions. Thermal protection mechanisms are often incorporated to prevent overheating during extended operation.
Mechanical integration involves selecting appropriate mounting methods, vibration isolation components, and transmission systems. Brush DC Motor performance can be optimized through proper alignment, gear selection, and load balancing.
Environmental exposure is another critical factor. Household appliances may expose motors to moisture, dust, grease, and temperature fluctuations. Brush DC Motor designs used in these applications often include protective housings, sealed bearings, and corrosion-resistant materials.Brush DC Motor Applications in Power Tools and DIY Equipment
Brush DC Motor Performance Requirements in Power Tools
Brush DC Motor is a core driving component in many power tools and DIY equipment where high torque, rapid acceleration, and reliable performance under variable load conditions are required. Power tools operate under demanding mechanical stresses, including sudden load changes, intermittent duty cycles, and frequent start-stop operation. Brush DC Motor addresses these demands through its inherent ability to deliver high starting torque and respond quickly to changes in supply voltage.
In handheld power tools, such as drills, screwdrivers, and rotary tools, Brush DC Motor supports both continuous rotation and pulsed operation. The predictable torque–speed characteristic of Brush DC Motor enables designers to tailor tool performance for drilling, fastening, grinding, or cutting tasks without complex electronic control systems. This allows for simpler tool architecture and improved reliability in harsh working environments.
DIY equipment often emphasizes user control and responsiveness. Brush DC Motor responds immediately to trigger input, providing intuitive speed modulation. This behavior enhances tool usability and aligns with user expectations in both professional and home workshop settings.
Brush DC Motor Use in Corded Power Tools
Corded power tools frequently employ Brush DC Motor due to its compatibility with rectified AC power and its ability to deliver sustained power output. Tools such as angle grinders, electric saws, sanders, and impact drills rely on Brush DC Motor to generate consistent mechanical energy during extended operation.
In corded tools, Brush DC Motor is typically powered through a rectifier and control circuit that converts AC mains voltage into DC. This configuration allows the motor to operate at high power levels while maintaining manageable thermal characteristics. The robust construction of Brush DC Motor supports prolonged use in demanding applications such as metal cutting, masonry drilling, and surface finishing.
Angle grinders utilize Brush DC Motor to achieve high rotational speeds required for cutting and grinding discs. The motor’s ability to maintain speed under load ensures consistent material removal and tool stability. In saws and sanders, Brush DC Motor provides the torque necessary to drive blades or sanding pads through resistant materials.
The mechanical simplicity of Brush DC Motor also facilitates easier servicing and brush replacement, which is a common maintenance practice in professional corded power tools.
Brush DC Motor Applications in Cordless Power Tools
Cordless power tools represent a major application area for Brush DC Motor, particularly in cost-sensitive product segments. Battery-powered drills, screwdrivers, hedge trimmers, and compact saws often incorporate Brush DC Motor due to its efficiency at low to moderate voltages and its ability to operate directly from battery packs.
Brush DC Motor designs used in cordless tools are optimized for battery efficiency and high torque output. The motor’s performance characteristics allow tools to deliver strong fastening or cutting force even as battery voltage drops during use. This behavior is particularly important in DIY equipment, where users expect consistent performance without complex battery management systems.
Speed control in cordless tools is commonly implemented using simple electronic switches and pulse-width modulation. Brush DC Motor responds well to these control methods, enabling variable speed triggers and torque adjustment features. This supports precise operation across a wide range of DIY tasks.
The compact size of Brush DC Motor enables ergonomic tool designs with balanced weight distribution. This is critical in handheld equipment, where prolonged use can lead to user fatigue if weight and vibration are not properly managed.
Brush DC Motor Integration in Rotary and Cutting Tools
Rotary and cutting tools rely heavily on Brush DC Motor for precise and powerful rotational motion. Devices such as rotary grinders, oscillating tools, and multi-function cutting systems require motors that can deliver stable speed and torque across diverse applications.
Brush DC Motor drives cutting discs, abrasive wheels, and oscillating attachments through direct coupling or gear reduction mechanisms. The motor’s high-speed capability supports fine material removal, while its torque characteristics allow it to handle resistance from dense or hard materials.
In oscillating multi-tools, Brush DC Motor is often paired with mechanical conversion systems that transform rotational motion into oscillatory movement. The consistent rotational output of Brush DC Motor ensures smooth oscillation and predictable cutting behavior.
DIY users often rely on rotary tools for detailed work, such as engraving, polishing, and trimming. Brush DC Motor enables fine speed control, allowing users to adjust tool performance based on material type and task precision.
Brush DC Motor Use in Drilling and Fastening Equipment
Drilling and fastening equipment represents one of the most common use cases for Brush DC Motor in both professional and DIY markets. Electric drills, impact drivers, and screwdrivers rely on Brush DC Motor to deliver torque and rotational speed suitable for drilling holes or driving fasteners into various materials.
Brush DC Motor provides the high starting torque required to overcome initial resistance when drilling into wood, metal, or masonry. Gearboxes are often used to modify motor output, enabling multiple speed and torque ranges. The predictable performance of Brush DC Motor simplifies gearbox design and torque control strategies.
In impact drivers, Brush DC Motor drives hammer mechanisms that generate rapid rotational impacts. The motor’s ability to withstand repeated high-load cycles supports the durability requirements of these tools.
DIY users benefit from the intuitive control provided by Brush DC Motor-powered drills, where trigger pressure directly influences motor speed. This direct relationship enhances user confidence and operational accuracy.
Brush DC Motor Applications in Outdoor and Garden DIY Equipment
Outdoor and garden DIY equipment also incorporates Brush DC Motor in applications such as electric trimmers, hedge cutters, small lawn tools, and portable blowers. These tools require motors that can operate in variable environmental conditions while delivering sufficient power for cutting and clearing tasks.
Brush DC Motor-driven garden tools benefit from the motor’s ability to deliver torque at low speeds, which is essential for cutting thick vegetation or operating under load. The rugged construction of Brush DC Motor supports exposure to dust, moisture, and temperature fluctuations commonly encountered in outdoor environments.
Portable blowers and sweepers use Brush DC Motor to drive fan assemblies that generate airflow for debris removal. High-speed motor operation enables compact fan designs and effective airflow generation.
Battery-powered garden tools rely on Brush DC Motor for cost-effective performance, particularly in entry-level and mid-range product categories. The simplicity of motor control reduces electronic complexity and improves tool reliability.
Brush DC Motor Thermal and Mechanical Design Considerations
Thermal management is a critical aspect of Brush DC Motor application in power tools and DIY equipment. High current draw during heavy load operation generates heat within the motor windings and brushes. Effective heat dissipation strategies are required to maintain performance and extend motor lifespan.
Power tool housings often incorporate ventilation channels that direct airflow over the Brush DC Motor during operation. Cooling fans may be integrated directly onto the motor shaft to enhance heat removal. Brush DC Motor designs optimized for power tools typically use heat-resistant insulation materials and robust brush assemblies.
Mechanical design considerations include vibration control, shaft alignment, and load distribution. Brush DC Motor must be securely mounted to withstand shock and impact during tool operation. Gearboxes and couplings are designed to minimize backlash and mechanical stress on the motor shaft.
Brush DC Motor Manufacturing and Service Factors in DIY Equipment
Manufacturers of power tools and DIY equipment value Brush DC Motor for its mature manufacturing ecosystem and well-established service practices. The availability of standardized Brush DC Motor components supports large-scale production and global distribution.
From a service perspective, Brush DC Motor allows for straightforward maintenance, including brush replacement and motor servicing. This is particularly important in professional tools that are expected to remain in service for extended periods.
The cost-effectiveness of Brush DC Motor supports competitive pricing in the DIY market, where affordability and performance must be carefully balanced. Manufacturers can offer multiple product tiers by varying motor specifications while maintaining a common design platform.
Brush DC Motor Applications in Industrial Automation Equipment
Brush DC Motor Role in Industrial Automation Systems
Brush DC Motor is widely used in industrial automation equipment where controlled motion, reliable torque output, and straightforward system integration are required. Industrial automation systems often consist of multiple subsystems working in coordination, including conveyors, actuators, material handling units, inspection devices, and auxiliary mechanisms. Brush DC Motor supports these systems by providing consistent electromechanical performance with relatively simple electrical and mechanical interfaces.
Automation equipment frequently operates in environments that demand predictable behavior under variable loads. Brush DC Motor offers linear torque–current characteristics, allowing engineers to estimate performance outcomes with high confidence. This predictability is particularly valuable in automation systems where repeatability and process stability are critical.
The compatibility of Brush DC Motor with common DC power supplies and basic motor controllers allows system integrators to implement motion solutions without complex drive electronics. This simplifies control architecture and reduces development effort in automation projects with constrained timelines or budgets.
Brush DC Motor Applications in Conveyor and Material Handling Equipment
Conveyor systems and material handling equipment represent a primary application area for Brush DC Motor in industrial automation. These systems require continuous or intermittent motion to transport products, components, or materials between processing stations.
Brush DC Motor drives conveyor belts, rollers, and transfer mechanisms through direct coupling or gear reduction systems. The high starting torque of Brush DC Motor allows conveyors to overcome static friction and load inertia, particularly in systems that handle heavy or unevenly distributed loads.
Speed control is an essential requirement in conveyor applications. Brush DC Motor enables precise speed adjustment through voltage variation or pulse-width modulation, allowing conveyors to synchronize with upstream and downstream automation processes. This capability supports applications such as packaging lines, assembly stations, and sorting systems.
In roller conveyors and accumulation systems, multiple Brush DC Motor units may be distributed along the conveyor path. The standardized sizing and mounting options of Brush DC Motor facilitate modular system design and scalability.
Brush DC Motor Use in Actuators and Linear Motion Systems
Actuators and linear motion systems in industrial automation frequently incorporate Brush DC Motor to generate controlled movement. These systems convert rotational motion into linear displacement using mechanisms such as lead screws, ball screws, rack-and-pinion assemblies, or belt-driven actuators.
Brush DC Motor provides the torque and speed necessary to drive these mechanical conversions efficiently. In applications such as automated gates, adjustable fixtures, and positioning devices, Brush DC Motor supports repeatable and smooth motion control.
Linear actuators powered by Brush DC Motor are commonly used in pick-and-place systems, workpiece positioning units, and material alignment devices. The straightforward control of Brush DC Motor simplifies integration with programmable logic controllers and industrial control systems.
Load variability is a common challenge in linear motion applications. Brush DC Motor responds predictably to changes in load, allowing control systems to compensate through current monitoring and feedback mechanisms.
Brush DC Motor Applications in Automated Assembly Equipment
Automated assembly equipment relies on coordinated motion to assemble components with accuracy and efficiency. Brush DC Motor is often used to drive auxiliary assembly functions such as part feeding, screw driving, pressing, and component alignment.
In screw driving systems, Brush DC Motor delivers the torque required to fasten components while enabling adjustable speed control. Gearboxes are typically used to tailor motor output for specific fastening requirements. The consistent torque characteristics of Brush DC Motor support reliable fastening performance.
Part feeders and vibratory systems may use Brush DC Motor to drive rotating discs or feeding mechanisms. The motor’s ability to operate continuously and handle variable loads supports consistent part delivery to assembly stations.
Assembly equipment often operates in repetitive cycles. Brush DC Motor designs used in these systems are selected for durability and resistance to wear under frequent start-stop operation.
Brush DC Motor Integration in Packaging Machinery
Packaging machinery incorporates Brush DC Motor to drive motion in filling, sealing, labeling, and conveying operations. These machines require precise timing and synchronization between mechanical components to ensure product quality and throughput.
Brush DC Motor is used to drive film rollers, conveyor belts, and labeling mechanisms. Speed consistency is essential in these applications to maintain alignment and registration of packaging materials.
In filling machines, Brush DC Motor may drive pumps or dosing mechanisms that control fluid or material flow. The predictable performance of Brush DC Motor supports accurate dosing and repeatable filling operations.
Packaging environments often involve exposure to dust, moisture, and temperature variations. Brush DC Motor designs used in packaging machinery typically include protective enclosures and sealed components to ensure reliable operation.
Brush DC Motor Applications in Inspection and Testing Equipment
Inspection and testing equipment in industrial automation relies on precise motion to position sensors, cameras, and test probes. Brush DC Motor supports these functions by enabling controlled movement with straightforward integration.
Motorized stages and positioning platforms use Brush DC Motor to adjust component alignment during inspection processes. The linear speed response of Brush DC Motor allows smooth and controlled positioning.
Testing equipment may incorporate Brush DC Motor to cycle components through test procedures, rotate parts for inspection, or actuate mechanical test fixtures. The ability of Brush DC Motor to operate at both low and high speeds supports a wide range of testing requirements.
Reliability and repeatability are critical in inspection systems. Brush DC Motor contributes to consistent performance through stable electrical and mechanical behavior.
Brush DC Motor Use in Industrial Robotics Subsystems
Industrial robotics systems often include multiple subsystems that rely on Brush DC Motor for motion. While primary robot joints may use advanced motor technologies, Brush DC Motor is commonly applied in peripheral and auxiliary robotic functions.
Examples include end-effector actuation, gripper mechanisms, tool changers, and conveyor interfaces. Brush DC Motor provides sufficient torque and controllability for these tasks without the need for complex drive electronics.
Grippers powered by Brush DC Motor use mechanical linkages to open and close gripping jaws. The predictable torque output supports secure and repeatable gripping of workpieces.
Tool changers and accessory mechanisms rely on Brush DC Motor to perform controlled engagement and disengagement operations within robotic cells.
Brush DC Motor Control and Interface in Automation Equipment
Control and interface considerations are critical when integrating Brush DC Motor into industrial automation equipment. These motors are typically controlled using basic motor drivers, relays, or transistor-based circuits.
Speed control is achieved through voltage regulation or pulse-width modulation, often managed by programmable logic controllers or industrial controllers. Direction control is implemented using H-bridge configurations.
Feedback mechanisms such as encoders or current sensors may be added to Brush DC Motor systems to enhance control accuracy. These feedback components enable monitoring of motor speed, position, and load conditions.
The simplicity of Brush DC Motor control interfaces supports rapid commissioning and troubleshooting in industrial environments.
Brush DC Motor Reliability and Maintenance in Industrial Settings
Industrial automation equipment is expected to operate reliably over long periods with minimal downtime. Brush DC Motor designs used in these applications are selected based on durability, brush life, and resistance to environmental factors.
Maintenance practices often include periodic inspection and replacement of brushes. The accessibility of Brush DC Motor components simplifies maintenance procedures and reduces service time.
Industrial facilities benefit from the widespread availability of replacement Brush DC Motor units and spare parts. This availability supports maintenance strategies that prioritize quick restoration of equipment functionality.
References / Sources
-
Hughes Publishing — “Electric Motors and Drives: Fundamentals, Types and Applications”
-
McGraw-Hill Education — “Electric Machinery Fundamentals”
-
CRC Press — “Electric Drives”
-
Wiley — “Design of Rotating Electrical Machines”
-
NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) — “Motors and Generators Standard (NEMA MG 1)”
-
Brush DC Motor Origins and Physical Foundations The Brush DC Motor is a pioneer in converting electrical energy into mechanical motion, and its history is closely intertwined with ...
READ MORE -
Who Is Still Using Brushed DC Motors These Days? Brushed DC motors in small appliances Despite the growing adoption of brushless motor technology, small appliances remain a major c...
READ MORE -
Brush DC Motor Applications in Consumer Electronics and Smart Devices Brush DC Motor Role in Consumer Electronics Design Brush DC Motor plays a critical role in the design and func...
READ MORE

 Eng
Eng  русский
русский Español
Español







